Ongoing Research Interests
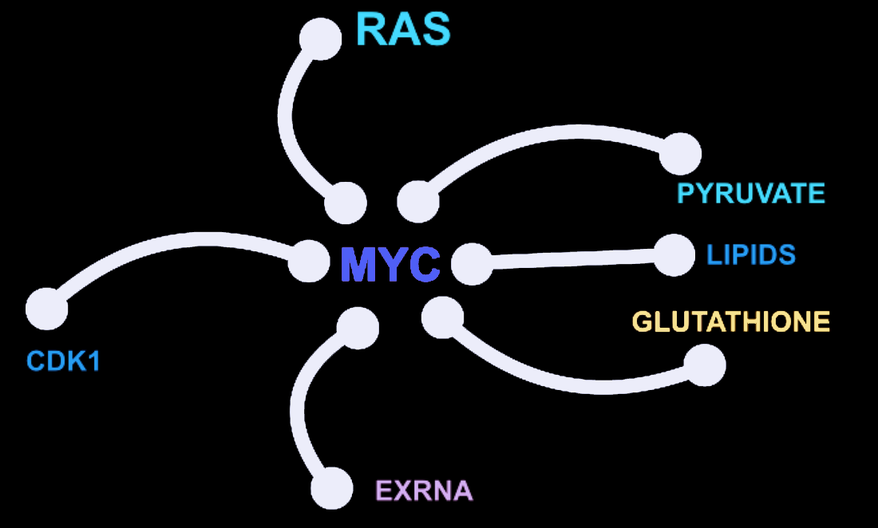
Activation of proto-oncogenes results in alterations of multiple signaling pathways, resulting in the rewiring of cell proliferation, metabolism and small RNA circuits which contribute to the tumorigenic state. Despite the discovery of numerous driver oncogenes in cancer, many of the most prevalent oncogenic alterations, such as activation of MYC or RAS cannot yet be readily blocked with small molecule inhibitors. Our laboratory seeks to elucidate how oncogenes reprogram signaling to uncover new vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
Cell CycleCyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are a conserved family of protein kinases that serve a central role in regulating the eukaryotic cell cycle. Tumor cells often develop a deregulated cell cycle program that may render their proliferation especially sensitive to inhibition of CDKs or other cell cycle kinases. We are testing the hypothesis that cell cycle arrest via selective mitotic kinase inhibition, such as CDK1, can induce an abortive cell cycle program in cancer cells driven by MYC, while sparing non-tumor cells.
|
MetabolismOncogenic signaling can reprogram metabolism within tumor celld, changing their dependence on specific nutrients or changing the cell's response to environmental stimuli. We seek to identify new metabolic pathways essential for primary tumor growth. Inhibition of these metabolic pathways may provide new cancer therapies.
|
Small RNAsMicroRNAs (miRNAs) and other small non-coding RNAs can regulate cell differentiation and are deregulated in a variety of human cancers. We seek to identify small RNAs that are critical for tumorigenesis and may regulate oncogene or tumor suppressor gene functions.
|
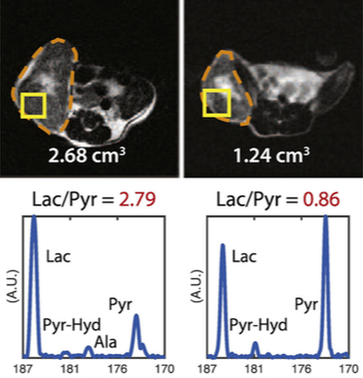
Metabolic ImagingOur studies have uncovered that metabolic changes can precede primary tumor formation and can also be detected prior to overt tumor regression. In vivo metabolic imaging thus allows for the identification of tumors at an early stage, can discern different oncogene signaling pathways, and can inform clinical use of and response to novel therapeutics. We seek to develop various metabolic imaging approach for early detection of cancers.
|
Oncogene CooperationHow do oncogenes cooperate to alter cell cycle, metabolism and apoptotic programs that drive tumor growth? Does oncogene cooperation provide us with novel targets for therapy?
|
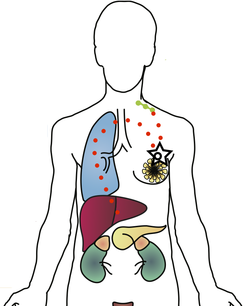
Tumor MetastasisMetastatic cancer is the single most urgent and difficult to treat challenge for patients. Our group seeks to discover unique vulnerabilities of metastatic tumor cells, using single cell sequencing and functional approaches. Furthermore, we seek to develop new model systems that will allow us to understand fundamental mechanisms of how tumor cells disseminate within the host.
|